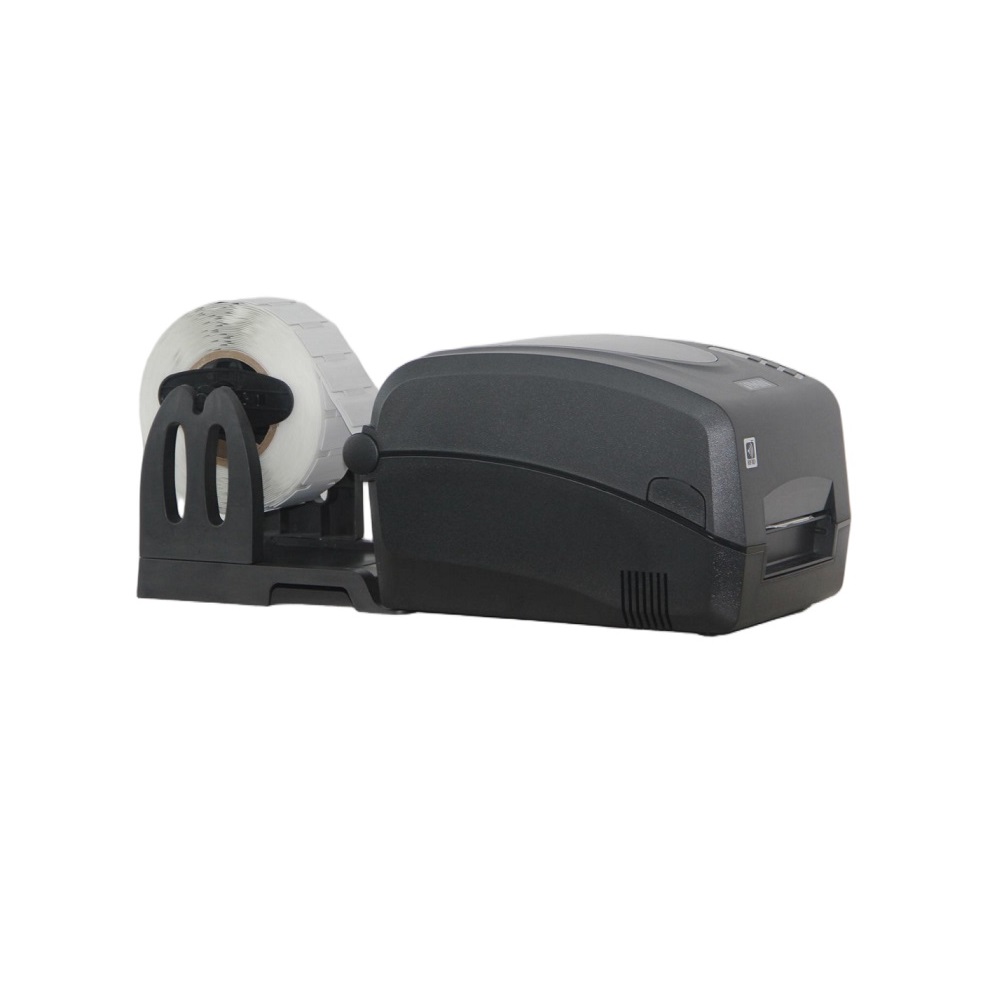
l The reader is designed with adjustable power settings, allowing measurement of induction range variations through power adjustments.
l Antenna dimensions: Larger antennas theoretically extend detection ranges but cause energy dispersion, requiring design tailored to specific application scenarios.
l Tag specifications: While larger tags provide greater energy capacity, practical requirements often necessitate special antenna designs or material modifications.
l Environmental impedance ratio: Antenna impedance matching varies across environments, with quality factor measurements from the reader providing clear data.
l Tag sensitivity: Measured through RSSI signal strength detection.
l Actual environmental sensitivity: Same as above.
l Frequency synchronization between reader and tag: Special applications may require frequency tuning.
l Co-channel interference: External noise detection enables effective interference assessment.