The core pain points and technological breakthroughs of cross-border e-commerce logistics
According to the General Administration of Customs, China's cross-border e-commerce transaction volume exceeded $2.8 trillion in 2024, a year-on-year increase of 23.5%, but the "efficiency bottleneck" and "security risks" in the logistics link still restrict the development of the industry:
• Low customs clearance efficiency: under the traditional manual verification mode, the average customs clearance time of cross-border parcels is more than 3 hours, and the delay rate is as high as 18% during the promotion period;
• Difficult to prevent counterfeiting and traceability: According to the statistics of the European Union Intellectual Property Office, 37% of counterfeit electronic products are circulated through cross-border channels, and less than 30% of consumers can prove their rights;
• High operating cost: the error rate of manual sorting is 1.2%, and the cost of re-delivery and claim settlement for each order due to error increases by 15 yuan on average, with annual loss exceeding 10 billion yuan.
In this context, RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, with its core advantages of "non-contact identification", "multi-tag group reading" and "full link traceability", is becoming a key technology to solve the pain points of cross-border logistics, and promoting the transformation of the industry from "human driven" to "digital driven".
I. Customs clearance efficiency revolution: from "stop inspection" to "seamless passage"
Traditional cross-border customs clearance requires three major steps: "document verification, unpacking inspection and information input", which is tedious and relies on manual labor. However, RFID technology realizes the automation of the whole customs clearance process through the combination of "digital label + intelligent verification", and the core breakthrough is reflected in three aspects:
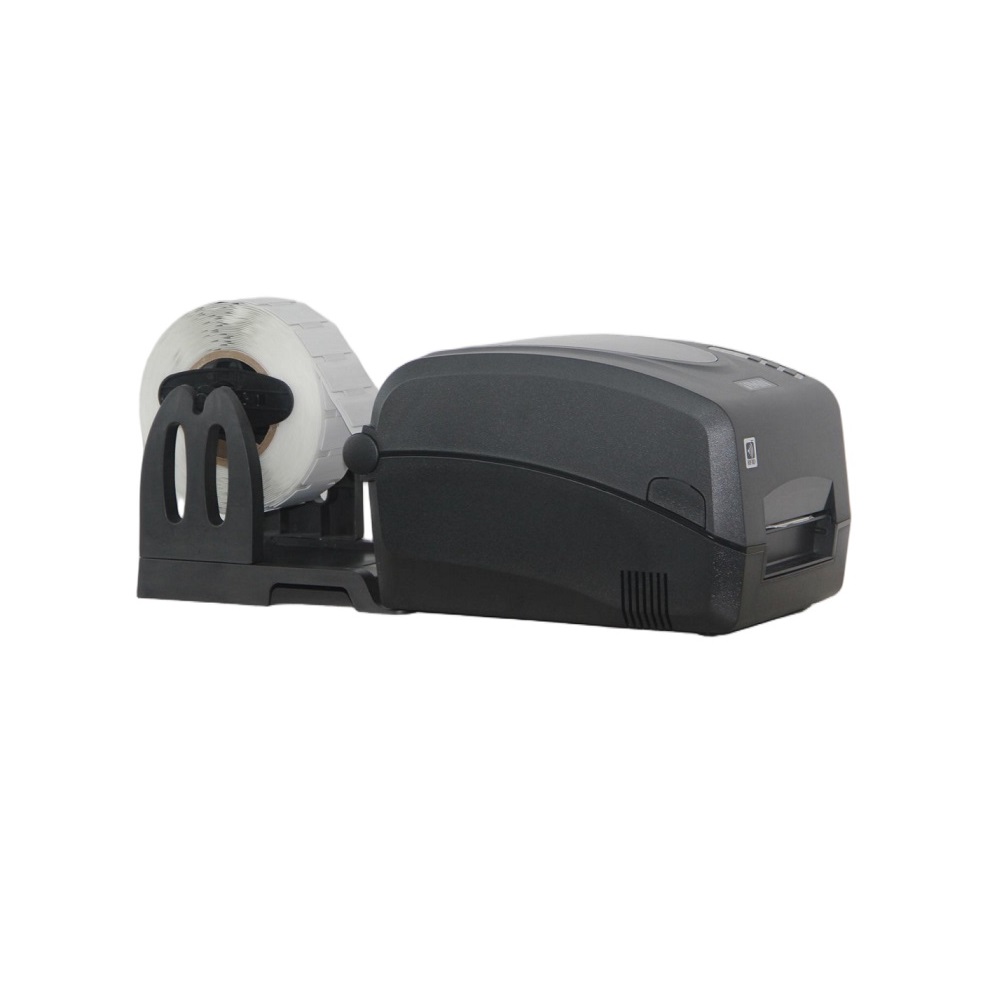
1. Passive tags: Give goods an "electronic ID card"
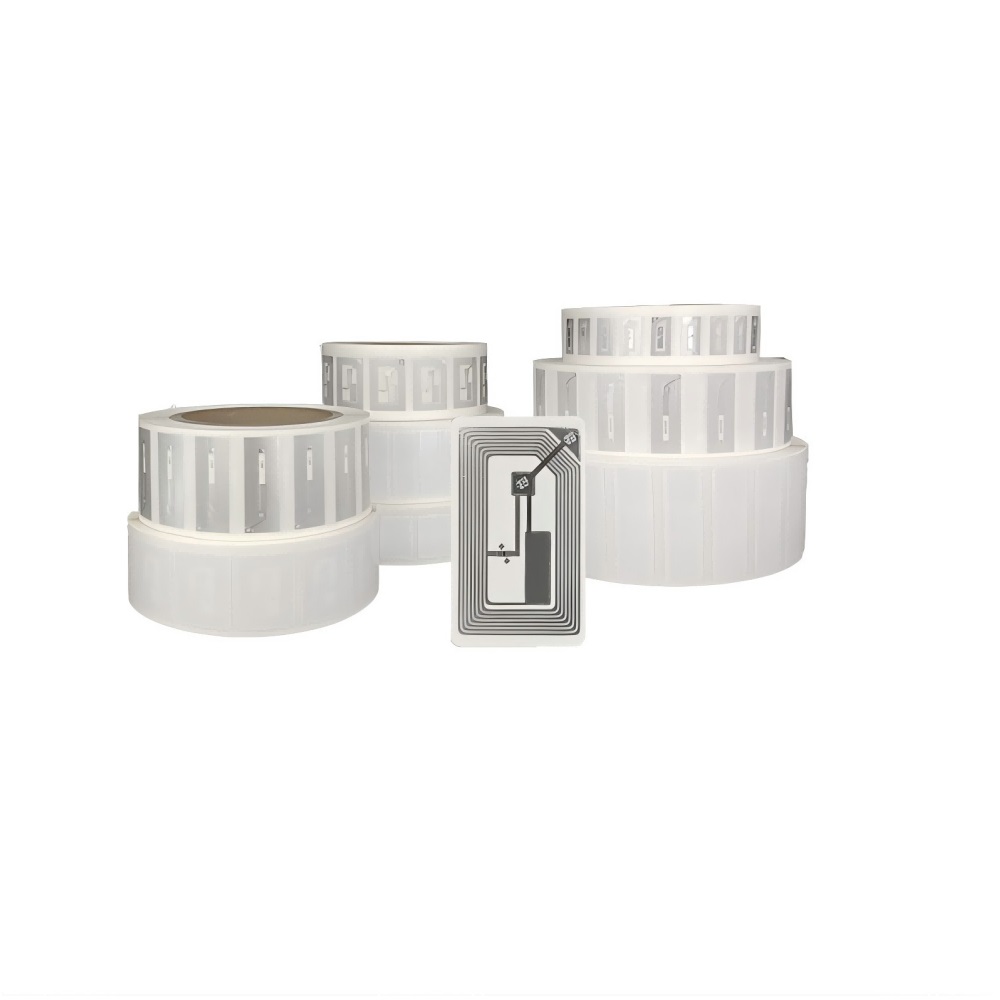
UHF anti-metallic passive tags (working frequency band 860-960MHz) are implanted on the surface of cross-border parcels or containers. The tags have unique ID and core product information (such as product code, declared value, origin, production batch) built in. They have three characteristics:
• Anti-environmental interference: waterproof, anti-fall, anti-metal packaging process, can work stably in extreme transportation environment of-30℃ to 70℃, label life up to 5 years;
• Low cost and popularity: The cost of a single label is as low as $0.03, which is suitable for large-scale application in general goods cross-border scenarios;
• Fast identification: Supports "simultaneous reading of multiple tags", a single reader can identify more than 300 tags per second, far exceeding the efficiency of traditional bar code "single scan".
2. Intelligent verification system: build a "seamless customs clearance" network
Taking the "electronic checkpoint system" of Shenzhen Customs and Cainiao Hong Kong eHub as an example, the coordination between RFID technology and hardware equipment achieves a leap in efficiency:
• Shenzhen Customs case: The URF520 industrial multi-channel reader is deployed at the customs clearance gate of trucks. The container label information can be read without stopping the vehicle, and the customs clearance time can be reduced from 3-5 minutes to less than 1 second when passing through at high speed. The processing capacity per lane is increased to 200 trucks per hour, which is 300% more efficient than the traditional mode;
• Cainiao Hong Kong eHub Case: After the full deployment of RFID in June 2025, the "seamless verification" process for cross-border parcels from unloading to warehousing will take only 1 minute (compared to 5 minutes with traditional manual scanning). During peak sales periods, the system handles over 500,000 items per day with 99.9% verification accuracy, effectively preventing customs clearance delays caused by human errors.
3. Blockchain collaboration: Achieve "data immutability"
We have jointly built a cross-border logistics blockchain platform with Ant Chain, Jingdong Technology and other enterprises. The data of 119 key nodes collected by RFID tags (such as sorting time, transportation temperature, customs clearance node and receipt information) are uploaded to the chain in real time, which has three values:
• Compliance and transparency: Customs, enterprises and consumers can query the flow of goods in real time to meet the regulatory requirements of different countries/regions (such as EU IOSS tax declaration, US FDA food traceability);
• Risk warning: When the goods deviate from the preset transportation route or exceed the temperature limit, the system will automatically trigger the sound and light warning. In 2024,12,000 abnormal parcels were intercepted through this mechanism, and the loss was recovered more than 30 million yuan;
• Dispute traceability: Once a wrong or missed delivery occurs, the responsible link can be quickly located through on-chain data, and the dispute processing time can be shortened from 72 hours to 4 hours.
II. Anti-counterfeiting and traceability closed loop: Give each product a "digital passport"
In cross-border e-commerce, counterfeit goods and unauthorized product distribution pose a shared challenge for both consumers and brands ——. In 2024, counterfeit product complaints accounted for 28% of total cross-border e-commerce complaints, directly impacting brand reputation and consumer trust. RFID technology provides dual safeguards through "physical anti-counterfeiting + digital encryption," establishing a closed-loop traceability system across the entire supply chain:
1. Physical anti-counterfeiting: from "anti-copying" to "anti-transfer"
Design differentiated physical anti-counterfeiting schemes according to the characteristics of different commodities:
• Fragile labels: High-value goods (such as luxury goods and 3C products) use "immediately destroyed" fragile substrate. Once the label is peeled off the surface of the goods, the internal circuit is immediately damaged and cannot be reused. In 2024, the interception rate of cross-border fake luxury goods increased to 97.3%;
• Dynamic color change labels: OPPO, Xiaomi and other brands use temperature-sensitive color RFID labels in the Southeast Asian market. When the goods circulate to unauthorized areas, the color of the labels changes automatically, and the number of reports of illegal goods decreased by 52% year on year;
• Tamper-resistant packaging: Ultrasonic sealing is used for pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and other categories, and the label and packaging are integrated into one. The anti-counterfeiting will be triggered when the package is damaged, and the number of complaints about counterfeit drugs across borders has decreased by 41%.
2. Digital encryption: from "querifiable" to "verifiable"
Each RFID tag has a unique electronic code built in and is bound to the product information through the AES-256 encryption algorithm. Consumers and regulators can verify it in two ways:
• NFC near field verification: use the NFC function of the phone to approach the label, and then jump to the official traceability page of the brand to view the whole process information of product production, transportation and customs clearance, with 100% accuracy;
• Code scanning verification: the label surface is printed with a unique code QR code, and consumers can complete the verification by scanning the code and entering the verification code. In 2024, the number of cross-border commodity traceability queries exceeded 50 million times, and the consumer trust increased to 89%.
3. Full chain storage: from "single point traceability" to "full cycle management"
Taking the cross-border import of milk powder as an example, the full cycle data recorded by RFID tags include:
1) Production process: ranch information, production batch and quality inspection report;
2) Transportation: shipping/air waybill number, transportation temperature (updated every 10 minutes), transfer nodes;
3) Customs clearance: customs declaration number, customs duty payment certificate and customs inspection record;
4) Sales link: distributor information, shelf time and sales channel.
The brand can monitor the flow of goods in real time through the background, and once abnormal circulation is found (such as expired goods, sales in unauthorized areas), the label "anti-counterfeiting invalidation" can be triggered remotely to curb fake goods and counterfeiting from the source.
III. Technical implementation guide: RFID solution selection for different cross-border scenarios
Cross-border logistics scenarios are complex and diverse (such as general goods, cold chain, high-value goods, bulk goods), so it is necessary to accurately select models according to the characteristics of goods, transportation links and regulatory requirements to avoid efficiency waste or high cost caused by "one size fits all".
Application scenarios | Proposed technical approach | Core advantage | Typical cases and results |
Cross-border goods (e.g. clothing, household goods) | UHF passive tag + fixed reader | High group reading efficiency (300+ tags per second) and cost as low as $0.03 per tag | Cainiao Hong Kong eHub: 300% improvement in storage verification efficiency and 0.03% error rate
|
Cold chain cross-border (e.g. vaccines, fresh food) | Anti-cold RFID tag + temperature sensor + industrial PDA | -30℃ to 70℃ stable working environment, temperature and humidity monitoring in real time | Cross-border vaccine transport: loss rate reduced from 0.3% to 0.02% |
High value goods (such as luxury goods, 3C)
| Fragile RFID tags + Blockchain storage + NFC verification | Transfer prevention and reuse, full chain traceability, consumers can verify independently | Cross-border luxury goods: 97.3% interception rate of fake goods, brand reputation increased by 28% |
Bulk goods (e.g. containers, vehicles)
| Active RFID tag + remote reader (10 m recognition)
| Dynamic tracking, support high speed mobile recognition (vehicle speed 60km/h can be recognized)
| Shenzhen Customs clearance for trucks: The clearance time has been reduced from 5 minutes to 1 second, and the daily processing capacity is 20,000 vehicles |
Core principles of selection:
1. Cost adaptation: Passive tags (low cost) are preferred for general goods scenarios, and active tags (strong functions) can be accepted for high-value scenarios;
2. Environmental adaptation: waterproof and low-temperature resistant labels should be selected for cold chain and humid environment, and anti-metal labels should be selected for metal surface products;
3. Regulatory adaptation: The EU, the United States and other regions should choose labels that meet local frequency band standards (such as 868MHz in the EU and 915MHz in the United States) to avoid customs clearance obstacles caused by frequency band incompatibility.
IV. Future trends: Building a "digital neural network" for global trade
When RFID technology is deeply integrated with 5G, edge computing and AI, cross-border logistics is upgrading from "passive tracking" to "active prediction". The three future development directions are worth paying attention to:
1. Predictive scheduling: from "dealing with congestion" to "avoiding congestion"
Real-time traffic data (e.g., number of vehicles passing through customs, parcel volume, transportation routes) collected by RFID tags are combined with AI algorithm to predict the logistics peak in the next 48 hours and allocate resources in advance:
• Cainiao has achieved real-time data synchronization between its Liege hub in Europe and its Hong Kong eHub, which reduced the clearance delay rate from 18% to 3% by adjusting the number of inspection windows 24 hours in advance through predictive models;
• Through the coordination of RFID tags and AGV robots, Amazon Logistics Center can realize real-time shelf position update and order matching prediction, which can shorten the sorting and preparation time from 2 hours to 30 minutes.
2. Multi-technology integration: from "single identification" to "multi-dimensional perception"
RFID tags will integrate more sensor functions (such as temperature and humidity, vibration, light) to achieve "full state monitoring" of goods:
• Cross-border fresh scene: The label can monitor the freshness of goods in real time (such as ethylene concentration), and automatically trigger the "priority delivery" instruction once it exceeds the threshold;
• Fragile goods cross-border scenario: The label has built-in vibration sensor. When the vibration exceeds the standard during transportation, it will immediately notify the logistics party to adjust the transportation speed and reduce the damage rate.
3. Global standardization: from "regional connectivity" to "global connectivity"
Currently, there are differences in RFID standards (band, data format) in different countries/regions, which restricts the efficiency of global logistics. In the future, international organizations (such as ISO and EPCGlobal) will promote the unification of standards and realize "one tag for the whole world":
• China has joined forces with ASEAN countries to promote "cross-border RFID standard mutual recognition", and will realize the data exchange of labels among the ten ASEAN countries by 2025, which is expected to further improve the cross-border customs clearance efficiency between China and ASEAN by 20%;
• UNCTAD is exploring a "Global RFID Logistics Data Platform" to promote customs data sharing among countries, with the goal of reducing the average delivery time for global cross-border orders from 72 hours to 48 hours.
The core value of RFID enabling cross-border logistics
The essence of the transformation of RFID technology to cross-border e-commerce is to break through the information gap between "goods, logistics, supervision and consumers" through the "digital ID card", and realize three core values:
1. Efficiency upgrade: The clearance time is compressed from 3 hours to 1 second, the sorting efficiency is increased by 300%, the error rate is reduced to 0.03%, and the logistics cost is directly reduced by 15%;
2. Security upgrade: The anti-counterfeiting rate was increased to 97.3%, the whole link traceability guaranteed the rights and interests of consumers, and the brand reputation was improved by 28%;
3. Experience upgrade: Consumers can independently verify the authenticity and flow of goods, and the "72-hour delivery" of cross-border orders has changed from a marketing slogan to a reality, and the user satisfaction has increased to 89%.
For cross-border e-commerce businesses, adopting RFID solutions has evolved from an optional choice to a survival imperative—— In the context of intensifying global trade competition, technology-driven efficiency and security advantages will become the core competitive edge for enterprises to capture market share. Looking ahead, as global standards converge and multiple technologies integrate, RFID will establish itself as the "digital neural network" of international trade, propelling cross-border logistics into a new era characterized by seamless connectivity, borderless operations, and worry-free experiences.